
In the last tutorial, we completed our Python installation and setup. It’s time to create your first program. So in this tutorial, we will learn How to create your first Python Program, Main Function ,Variables in Python and Strings. Also at the end of this tutorial , I have provided one assignment. Try to solve it by your own.
Creating First Program
Step 1) Open PyCharm Editor. You can see the introductory screen for PyCharm. To create a new project, click on “Create New Project”. Give name to project . As we are not creating any project , we will write number of programs in a single Project.
Step 2) Now Go up to the “File” menu and select “New”. Next, select “Python File”.
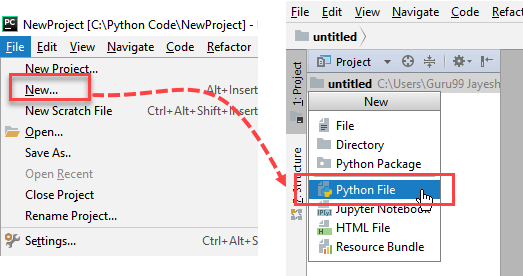
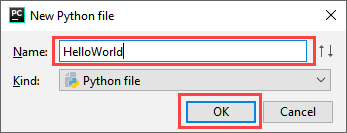
Step 3) A new pop up will appear. Now type the name of the file you want (Here we give “HelloWorld”) and hit “OK”.
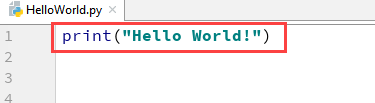
Step 4) Now type a simple program – print (‘Hello World!’).
Step 5) Run the Program and you will get output at console .
2. Main Function in Python
Main function is the entry point of any program. But python interpreter executes the source file code sequentially and doesn’t call any method if it’s not part of the code. But if it’s directly part of the code then it will be executed when the file is imported as a module.
3.Variables in Python
Every value in Python has a datatype. Different data types in Python are Numbers, List, Tuple, Strings, Dictionary, etc .
- Variables can be declared by any name .
- Variables can be re-declared even after you have declared them for once.
- In Python you cannot concatenate string with number directly, you need to declare them as a separate variable, and after that, you can concatenate number with string.
- Declare local variable when you want to use it for current function.
- Declare Global variable when you want to use the same variable for rest of the program.
- To delete a variable, it uses keyword “del”.
4. Strings
In Python everything is object and string are an object too. Python string can be created simply by enclosing characters in the double quote. ..For example: var = “Hello World!”
Python does not support a character type, these are treated as strings of length one, also considered as sub-string. We use square brackets for slicing along with the index or indices to obtain a sub-string.
String Operators:
| Operator | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| [ ] | Slice- it gives the letter from the given index | ||
| [ : ] | Range slice-it gives the characters from the given range | ||
| in | Membership-returns true if a letter exist in the given string | ||
| not in | Membership-returns true if a letter exist is not in the given string | ||
| r/R | Raw string suppresses actual meaning of escape characters. | ||
| % – Used for string format | %r – It insert the canonical string representation of the object (i.e., repr(o)) %s- It insert the presentation string representation of the object (i.e., str(o)) %d- it will format a number for display | ||
| + | It concatenates 2 strings | ||
| * | Repeat |
- replace() method returns a copy of the string in which the values of old string have been replaced with the new value
- lower() – Returns string in lower case.
- upper() – Returns string in upper case.
- join()– It is a more flexible way for concatenating string. With join function, you can add any character into the string.
- reversed() – Returns reversed string.
- split(‘ ‘)– Returns two strings from one string by splitting it with mentioned character in single quote.
Assignment:
1.Addition of 2 numbers 2.Addition of 2 numbers by taking input from user 3.Calculate simple interest 4.Program which accepts the radius of a circle from the user and compute the area. 5.Program which accepts the user's first and last name and print them in reverse order with a space between them 6.Program that accepts an integer (n) and computes the value of n+nn+nnn. Click here For Solution....


Leave a comment