
In this tutorial, we will see Python tuples, dictionary, operators and functions.
Python Tuples:
A tuple is just like a list of a sequence of immutable python objects. The difference between list and tuple is that list are declared in square brackets and can be changed while tuple is declared in parentheses and cannot be changed. However, you can take portions of existing tuples to make new tuples.
Tuple Example
Tup = ('Jan','feb','march')
To write an empty tuple, you need to write as two parentheses containing nothing-
tup1 = ();
For writing tuple for a single value, you need to include a comma, even though there is a single value. Also at the end you need to write semicolon as shown below.
Tup1 = (50,);
Tuple indices begin at 0, and they can be concatenated, sliced and so on.
A tuple is just like a list of a sequence of immutable python objects. The difference between list and tuple is that list are declared in square brackets and can be changed while tuple is declared in parentheses and cannot be changed. However, you can take portions of existing tuples to make new tuples.
Tuple Syntax
Tup = ('Jan','feb','march')
To write an empty tuple, you need to write as two parentheses containing nothing-
tup1 = ();
For writing tuple for a single value, you need to include a comma, even though there is a single value. Also at the end you need to write semicolon as shown below.
Tup1 = (50,);
Tuple indices begin at 0, and they can be concatenated, sliced and so on.
Packing and Unpacking:
In packing, we place value into a new tuple while in unpacking we extract those values back into variables.
e.g. tup= { "Sveri", 6220, "Pandharpur"} #packing
{clg_name , code, place} = tup #Unpacking
Built-in functions with Tuple:
To perform different task, tuple allows you to use many built-in functions like all(), any(), enumerate(), max(), min(), sorted(), len(), tuple(), etc.
Advantages of tuple over list:
- Iterating through tuple is faster than with list, since tuples are immutable.
- Tuples that consist of immutable elements can be used as key for dictionary, which is not possible with list
- If you have data that is immutable, implementing it as tuple will guarantee that it remains write-protected
Dictionary:
Dictionaries are another example of a data structure. A dictionary is used to map or associate things you want to store the keys you need to get them. A dictionary in Python is just like a dictionary in the real world. Python Dictionary are defined into two elements Keys and Values.
- Keys will be a single element
- Values can be a list or list within a list, numbers, etc.
Example for Python Dictionary:
Dict = { ' Tim': 18, xyz,.. }
Dictionary is listed in curly brackets, inside these curly brackets, keys and values are declared. Each key is separated from its value by a colon (:) while each element is separated by commas.
Properties of Dictionary Keys
- More than one entry per key is not allowed ( no duplicate key is allowed)
- The values in the dictionary can be of any type while the keys must be immutable like numbers, tuples or strings.
- Dictionary keys are case sensitive- Same key name but with the different case are treated as different keys in Python dictionaries.
Python Dictionary Methods:
| Method | Description | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| copy() | Copy the entire dictionary to new dictionary | dict.copy() |
| update() | Update a dictionary by adding a new entry or a key-value pair to an existing entry or by deleting an existing entry. | Dict.update([other]) |
| items() | Returns a list of tuple pairs (Keys, Value) in the dictionary. | dictionary.items() |
| sort() | You can sort the elements | dictionary.sort() |
| len() | Gives the number of pairs in the dictionary. | len(dict) |
| cmp() | Compare values and keys of two dictionaries | cmp(dict1, dict2) |
| Str() | Make a dictionary into a printable string format | Str(dict) |
Operators
| Operators | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ** | Exponent |
| *, /, //, % | Multiplication, Division, Floor division, Modulus |
| +, – | Addition, Subtraction |
| <= < > >= | Comparison operators |
| =, %=, /=, //=, -=, +=, *=, **= | Assignment Operators |
| is ,is not | Identity operators |
| in, not in | Membership operators |
| not ,or, and | Logical operators |
What is a Function in Python?
A Functions in Python are used to utilize the code in more than one place in a program, sometimes also called method or procedures. Python provides you many inbuilt functions like print(), but it also gives freedom to create your own functions.
How to define and call a function in Python?
Function in Python is defined by the “def ” statement followed by the function name and parentheses { }
Arguments in Functions:
The argument is a value that is passed to the function when it’s called. In other words on the calling side, it is an argument and on the function side it is a parameter. Lets see how Python Args works –
Case 1) Arguments are declared in the function definition. While calling the function, you can pass the values for that args as shown below

Case 2) To declare a default value of an argument, assign it a value at function definition.
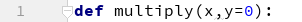
Example: x has no default values. Default values of y=0. When we supply only one argument while calling multiply function, Python assigns the supplied value to x while keeping the value of y=0. Hence the multiply of x*y=0

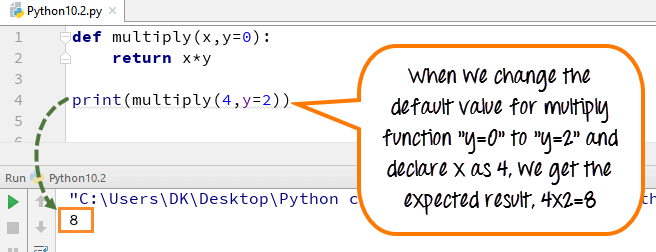
Case 3) This time we will change the value to y=2 instead of the default value y=0, and it will return the output as (4×2)=8.
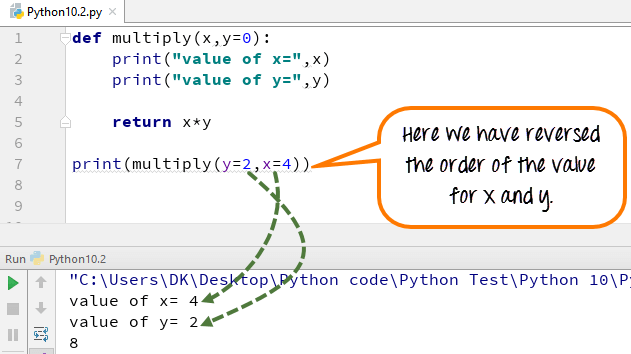
Case 4) You can also change the order in which the arguments can be passed in Python. Here we have reversed the order of the value x and y to x=4 and y=2.
Case 5) Multiple Arguments can also be passed as an array. Here in the example we call the multiple args (1,2,3,4,5) by calling the (*args) function.
Thats all about today’s learning . Try below assignments for hands -on coding.
1. Python Program for How to check if a given number is Fibonacci number? 2.Program to accept the strings which contains all vowels. 3.Program to Split the array and add the first part to the end 4.Program to check if a string is palindrome or not. 5.Program to find the sum of all Items in the dictionary. Click here for Solution...


Leave a comment