TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol and it is a suite of protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet. It requires a little central management and is designed to make networks reliable with ability to recover failures.
There are 4 layers in TCP/IP:
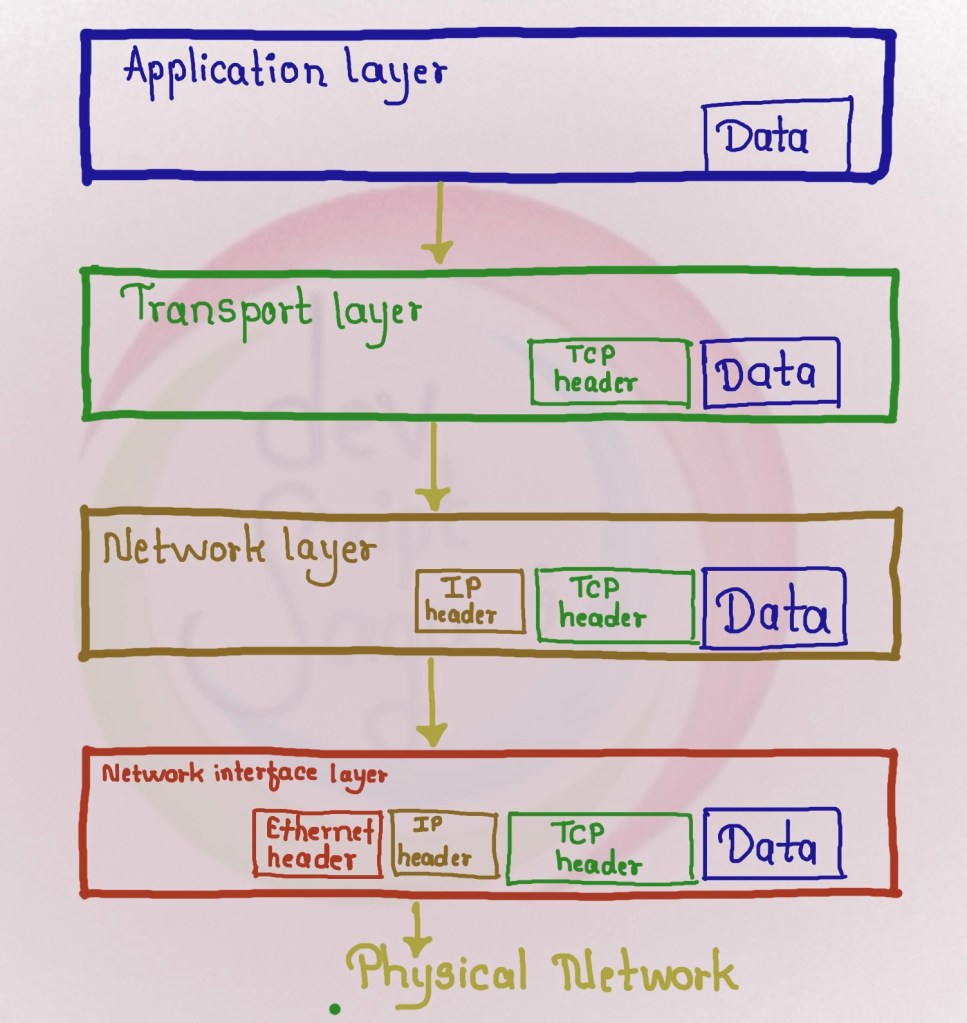
- Application Layer:
- Provides standardized data exchange
- Payload is actual application data
- Protocols: HTTP, FTP, Post Office Protocol3 , SMTP
- Transport layer:
- Maintains end-to-end communications across networks
- Protocols: TCP, UDP
- TCSP handles communication between hosts and provides flow control and reliability
- Network Layer:
- Also called Internet Layer
- Deals with packets
- Connects independent network to transport packets
- Protocols: IPV4, IPV6 and Internet control Message Protocol
- Network interface layer:
- Also called as, Physical layer or Data Link layer
- Consists of protocols that operate only on a link: the network component that interconnects hosts in the network
- Protocols: Ethernet for local area network, Address Resolution Protocol
The main drawback of TCP/IP is, it is not easy to replace protocols involved and it is vulnerable to synchronization attack which is type of DOS(Denial-of-service).


Leave a comment